Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Configuration and Styling¶
This example demonstrates how to configure PubliPlots using rcParams, set global styles, and customize various plotting parameters.
import publiplots as pp
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Understanding rcParams¶
PubliPlots uses an rcParams system similar to matplotlib and seaborn. You can access both matplotlib parameters and PubliPlots-specific parameters through the same unified interface.
# View some default PubliPlots parameters
print("PubliPlots Custom Parameters:")
print(f" Default color: {pp.rcParams['color']}")
print(f" Default alpha: {pp.rcParams['alpha']}")
print(f" Default capsize: {pp.rcParams['capsize']}")
print(f" Hatch mode: {pp.rcParams['hatch_mode']}")
print("\nMatplotlib Parameters (via pp.rcParams):")
print(f" Figure size: {pp.rcParams['figure.figsize']}")
print(f" Line width: {pp.rcParams['lines.linewidth']}")
print(f" Font size: {pp.rcParams['font.size']}")
print(f" DPI: {pp.rcParams['savefig.dpi']}")
PubliPlots Custom Parameters:
Default color: #5d83c3
Default alpha: 0.1
Default capsize: 0.0
Hatch mode: 1
Matplotlib Parameters (via pp.rcParams):
Figure size: [6.4, 4.8]
Line width: 1.5
Font size: 10.0
DPI: figure
Global Style Settings¶
PubliPlots provides two pre-configured styles: - notebook_style: For interactive work (larger figures, bigger fonts) - publication_style: For final manuscripts (compact, print-ready)
# Create sample data for demonstration
np.random.seed(100)
sample_data = pd.DataFrame({
'category': np.repeat(['A', 'B', 'C'], 10),
'value': np.concatenate([
np.random.normal(50, 8, 10),
np.random.normal(70, 10, 10),
np.random.normal(85, 12, 10),
])
})
# Notebook style
pp.set_notebook_style()
print("\nNotebook Style Settings:")
print(f" Figure size: {pp.rcParams['figure.figsize']}")
print(f" Font size: {pp.rcParams['font.size']}")
print(f" DPI: {pp.rcParams['savefig.dpi']}")
fig, ax = pp.barplot(
data=sample_data,
x='category',
y='value',
title='Notebook Style (Interactive Work)',
errorbar='se',
palette='pastel'
)
plt.show()
# Publication style
pp.set_publication_style()
print("\nPublication Style Settings:")
print(f" Figure size: {pp.rcParams['figure.figsize']}")
print(f" Font size: {pp.rcParams['font.size']}")
print(f" DPI: {pp.rcParams['savefig.dpi']}")
fig, ax = pp.barplot(
data=sample_data,
x='category',
y='value',
title='Publication Style (Print-Ready)',
errorbar='se',
palette='pastel'
)
plt.show()
# Reset to default
pp.reset_style()
Notebook Style Settings:
Figure size: [6.0, 4.0]
Font size: 12.0
DPI: 300.0
Publication Style Settings:
Figure size: [3.0, 1.8]
Font size: 8.0
DPI: 600.0
Customizing Individual Parameters¶
You can customize any parameter by setting it through pp.rcParams.
# Set custom defaults
pp.rcParams['color'] = '#E67E7E' # Change default color to red
pp.rcParams['alpha'] = 0.3 # Increase default transparency
pp.rcParams['capsize'] = 0.15 # Larger error bar caps
pp.rcParams['hatch_mode'] = 2 # Medium density hatch patterns
# Also customize matplotlib parameters
pp.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8, 5) # Wider figures
pp.rcParams['lines.linewidth'] = 2.5 # Thicker lines
pp.rcParams['font.size'] = 11 # Slightly larger font
# Create plot with custom defaults
fig, ax = pp.barplot(
data=sample_data,
x='category',
y='value',
title='Plot with Custom rcParams',
errorbar='se',
)
plt.show()
# Reset to default
pp.reset_style()
pp.set_notebook_style()
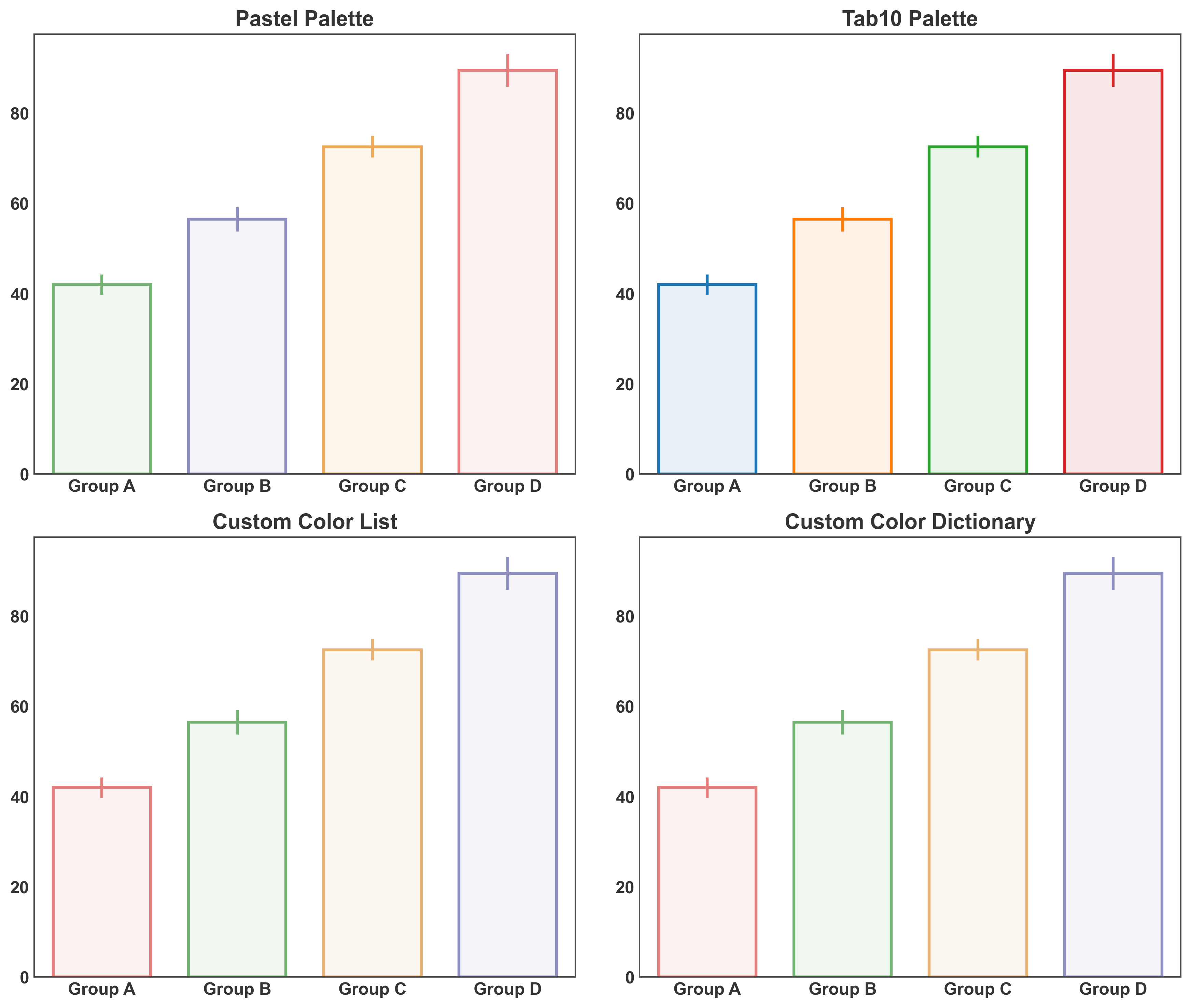
Using Color Palettes¶
PubliPlots provides easy access to color palettes.
# Create data for palette demonstration
palette_data = pd.DataFrame({
'group': np.repeat(['Group A', 'Group B', 'Group C', 'Group D'], 12),
'measurement': np.concatenate([
np.random.normal(45, 7, 12),
np.random.normal(60, 8, 12),
np.random.normal(75, 9, 12),
np.random.normal(90, 10, 12),
])
})
# Using built-in palettes
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 10))
# Pastel palette
pp.barplot(
data=palette_data,
x='group',
y='measurement',
hue='group',
palette='pastel',
errorbar='se',
title='Pastel Palette',
ax=axes[0, 0]
)
# Tab10 palette
pp.barplot(
data=palette_data,
x='group',
y='measurement',
hue='group',
palette='tab10',
errorbar='se',
title='Tab10 Palette',
ax=axes[0, 1]
)
# Custom color list
custom_colors = ['#E67E7E', '#75B375', '#E6B375', '#8E8EC1']
pp.barplot(
data=palette_data,
x='group',
y='measurement',
hue='group',
palette=custom_colors,
errorbar='se',
title='Custom Color List',
ax=axes[1, 0]
)
# Custom color dictionary
custom_dict = {
'Group A': '#E67E7E',
'Group B': '#75B375',
'Group C': '#E6B375',
'Group D': '#8E8EC1'
}
pp.barplot(
data=palette_data,
x='group',
y='measurement',
hue='group',
palette=custom_dict,
errorbar='se',
title='Custom Color Dictionary',
ax=axes[1, 1]
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Context-Based Styling¶
Temporarily override parameters for specific plots without changing global settings.
# Create sample scatter data
np.random.seed(200)
scatter_data = pd.DataFrame({
'x': np.random.randn(80),
'y': np.random.randn(80),
'category': np.random.choice(['Type 1', 'Type 2', 'Type 3'], 80)
})
# Plot 1: Default settings
fig, ax = pp.scatterplot(
data=scatter_data,
x='x',
y='y',
hue='category',
title='Default Settings',
palette='pastel',
alpha=0.2,
)
plt.show()
# Plot 2: Override alpha and color for this plot only
fig, ax = pp.scatterplot(
data=scatter_data,
x='x',
y='y',
hue='category',
title='Custom Alpha (Higher Opacity)',
palette='pastel',
alpha=0.5, # Override default alpha just for this plot
)
plt.show()
Saving Figures with Custom Settings¶
Control output quality and format when saving figures.
# Create a sample figure
fig, ax = pp.barplot(
data=sample_data,
x='category',
y='value',
title='Sample Figure for Saving',
errorbar='se',
palette='pastel'
)
# Save with different settings (uncomment to actually save)
# pp.savefig(fig, 'figure_low_res.png', dpi=150) # Lower resolution
# pp.savefig(fig, 'figure_high_res.png', dpi=300) # High resolution
# pp.savefig(fig, 'figure_vector.pdf') # Vector format (PDF)
# pp.savefig(fig, 'figure_vector.svg') # Vector format (SVG)
print("Figure saving examples (commented out to prevent file creation)")
print(" - PNG at 150 DPI (web/presentations)")
print(" - PNG at 300 DPI (publications)")
print(" - PDF (vector, editable)")
print(" - SVG (vector, web-friendly)")
plt.show()
Figure saving examples (commented out to prevent file creation)
- PNG at 150 DPI (web/presentations)
- PNG at 300 DPI (publications)
- PDF (vector, editable)
- SVG (vector, web-friendly)
Best Practices Summary¶
Use notebook_style() for interactive work and exploration
Switch to publication_style() when preparing final figures
Set global defaults with pp.rcParams for consistency
Override parameters per-plot when needed using function arguments
Use color palettes for consistent coloring across figures
Save in vector formats (PDF/SVG) for publications
Use hatch patterns for black-and-white publications
print("\nConfiguration complete!")
Configuration complete!
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.794 seconds)